In today’s fast-paced world, where convenience often takes precedence over nutrition, maintaining a healthy diet can seem like a daunting challenge. However, the significance of healthy eating cannot be overstated. It is one of the simplest yet most profound ways to influence both physical and mental well-being. The foods we choose to consume play a critical role in our overall health, from preventing chronic diseases to boosting our energy levels and enhancing our mood. In this article, we will explore various categories of healthy foods and their numerous benefits, alongside practical tips on how to incorporate them into daily meals.
What is Healthy Food?
Healthy foods are nutrient-dense, meaning they provide a high number of essential nutrients for relatively few calories. These nutrients include vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, healthy fats, and fiber. Eating a diet rich in these nutrients supports various bodily functions, including immune defense, metabolism, and heart health. In contrast, unhealthy foods, such as highly processed and refined products, are often loaded with sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, contributing to health issues like obesity, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes.
The Benefits of Healthy Eating
1. Weight Management
Eating healthy foods helps with weight control by allowing the body to regulate hunger and fullness cues more effectively. Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats are more satisfying than sugary or processed foods, helping prevent overeating. A diet high in nutrient-rich foods enables a person to meet their energy needs without the excess calories that lead to weight gain.
2. Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
A healthy diet can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, cancer, and hypertension. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, nuts, and leafy greens, protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress. Consuming a diet low in processed foods and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains lowers bad cholesterol and regulates blood pressure, further protecting heart health.
3. Improved Mental Health
The mind and body are closely linked, and food choices affect mental well-being as much as physical health. A growing body of research indicates that diets rich in whole foods, such as the Mediterranean diet, can reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon and walnuts play a crucial role in brain function, mood regulation, and cognitive health.
4. Enhanced Energy Levels
Healthy eating improves energy levels by providing the body with necessary nutrients and stable sources of fuel. Complex carbohydrates such as brown rice, whole wheat bread, and quinoa release glucose slowly, providing long-lasting energy without blood sugar spikes. Consuming an appropriate balance of protein, fats, and carbohydrates ensures that energy levels remain steady throughout the day.
5. Better Digestive Health
Fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and seeds support digestive health by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. They also encourage the growth of healthy gut bacteria, which play a crucial role in immune function and overall well-being. Fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi offer probiotics, beneficial bacteria that enhance gut health.
Key Categories of Healthy Foods
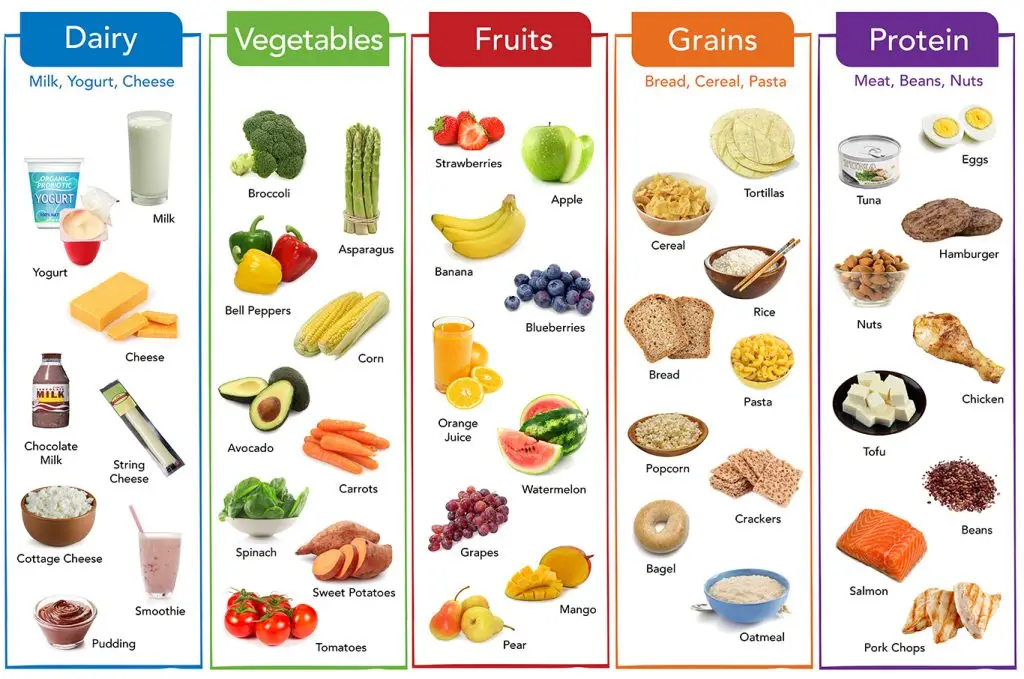
Let’s break down some of the major categories of foods that should form the foundation of a healthy diet.
1. Fruits and Vegetables
a. The cornerstone of any healthy diet, fruits and vegetables are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber. They provide a wide range of health benefits, including lowering blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke, preventing certain cancers, and improving digestive health.
b. Fruits such as berries, oranges, apples, and bananas are rich in vitamins C and A, while vegetables like spinach, kale, and broccoli are loaded with folate, vitamin K, and iron. Aim to eat a variety of colors to ensure a diverse intake of nutrients.
c. Tips to Incorporate More Fruits and Vegetables:
- Add spinach or kale to your morning smoothie.
- Include a side salad with lunch or dinner.
- Snack on fruits like apples, grapes, or carrot sticks during the day.
- Experiment with roasted vegetables like sweet potatoes, Brussels sprouts, and bell peppers.
2. Whole Grains
a. Whole grains are a key component of a balanced diet, providing essential nutrients such as fiber, vitamins B and E, iron, and magnesium. Unlike refined grains, which have been stripped of their nutrient-rich outer layers, whole grains retain all parts of the grain, offering more fiber and health benefits. Whole grains help maintain steady blood sugar levels, reduce inflammation, and support heart health.
b. Examples of whole grains include brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley, and whole wheat products. Switching from refined grains like white bread, white rice, and sugary cereals to their whole grain counterparts is a simple yet impactful dietary shift.
c. Tips to Include Whole Grains:
- Choose oatmeal over sugary breakfast cereals.
- Replace white rice with brown rice or quinoa.
- Opt for whole-grain bread and pasta instead of refined versions.
- Use whole wheat flour when baking.
3. Lean Proteins
a. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, making it a crucial part of a healthy diet. Lean proteins such as poultry, fish, tofu, beans, and legumes provide the necessary amino acids without excessive saturated fats found in processed or fatty meats. Consuming protein helps keep you feeling full longer, supports muscle health, and contributes to metabolic functions.
b. Fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are particularly beneficial, as they are rich in omega-3 fatty acids that improve heart and brain health. Plant-based proteins like lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and quinoa offer fiber and are excellent for vegetarians or those looking to reduce meat consumption.
c. Tips for Adding Lean Proteins:
- Grill or bake chicken and fish instead of frying them.
- Add beans or lentils to salads, soups, or stews.
- Replace red meat with plant-based proteins like tempeh or tofu.
- Snack on Greek yogurt, which is high in protein.
4. Healthy Fats
a. Not all fats are bad! In fact, healthy fats are necessary for brain function, hormone production, and nutrient absorption. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, found in foods such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, are heart-healthy and can reduce cholesterol levels.
b. Omega-3 fatty acids, primarily found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, are particularly beneficial for reducing inflammation and supporting cardiovascular health. On the other hand, trans fats and excessive saturated fats (from fried foods, baked goods, and processed snacks) should be limited, as they can increase the risk of heart disease.
c. Tips to Add Healthy Fats:
- Drizzle olive oil over salads and roasted vegetables.
- Include a handful of nuts or seeds in your snack rotation.
- Add avocado slices to sandwiches or toast.
- Choose fatty fish like salmon or trout twice a week.
5. Dairy and Dairy Alternatives
a. Dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese are rich in calcium, vitamin D, and protein, which are essential for bone health. However, if you’re lactose intolerant or follow a plant-based diet, there are plenty of dairy alternatives that offer similar benefits. Almond milk, soy milk, and fortified plant-based yogurts provide calcium and vitamin D without the lactose.
b. Greek yogurt is a particularly nutritious choice, as it’s higher in protein than regular yogurt and can be topped with fruits, nuts, or seeds for a healthy snack.
c. Tips for Dairy and Dairy Alternatives:
- Opt for low-fat or fat-free dairy products when possible.
- Add Greek yogurt to smoothies for an extra protein boost.
- Try plant-based milks like almond, soy, or oat milk as substitutes for dairy.
- Use cottage cheese or ricotta as a base for savory or sweet snacks.
Practical Tips for Eating Healthy
Eating a healthy diet doesn’t have to be complicated or restrictive. Here are some practical tips for incorporating healthy foods into your lifestyle:
- Plan Your Meals: Take time to plan your meals for the week. This makes it easier to choose healthy options and avoid last-minute takeout or unhealthy snacks.
- Cook at Home: Preparing meals at home gives you control over ingredients, portion sizes, and cooking methods. It’s also a great way to try new healthy recipes.
- Limit Processed Foods: Cut back on processed foods that are high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium. Focus on whole, natural foods.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is essential for digestion, metabolism, and overall health. Avoid sugary drinks and limit alcohol consumption.
- Mindful Eating: Pay attention to your hunger and fullness cues. Eat slowly, and savor your food to avoid overeating.
Conclusion
Incorporating a variety of healthy foods into your diet is one of the most effective ways to improve your physical and mental well-being. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats offers numerous benefits, from preventing chronic diseases to enhancing mood and energy levels. Making mindful food choices and adopting healthy eating habits can lead to a more vibrant and healthier life. Remember, it’s not about perfection—it’s about progress toward a healthier, more nourishing lifestyle.





Anonymous
amazing article